what causes eczema in adults
Eczema: what are the causes and how do you treat it?
Eczema is one of the most common skin conditions: one in five children and one in twenty adults suffer from it. Eczema itches, keeps you from sleeping and can cause infections. But fortunately, there's a lot you can do to naturally alleviate the symptoms of eczema.
What is eczema?
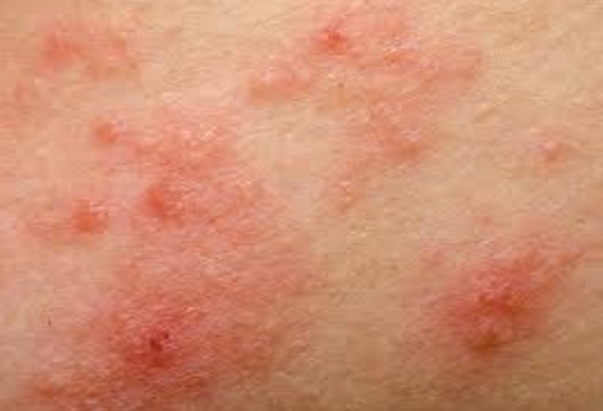
Eczema is a collective term for a large number of different skin conditions that result in itchy skin rashes. This non-contagious, chronic inflammation of the skin is characterized by dry, red, scaly and itchy patches on the skin. You can get eczema at any age, but eczema is more common in children than in adults. Most children grow over it, however, although they often retain dry skin or may still be susceptible to an eczema attack later in life.
What types of eczema are there?
Depending on the cause, form and location, we distinguish different types of eczema. The most common type of eczema is atopic dermatitis, but there are numerous other types, such as irritant dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, dishydrotic eczema, nummular eczema and seborrheic eczema. Read how to remove pimples naturally and permanetly
The best known types of eczema are :
Seborrheic eczema
Seborrheic eczema occurs mainly on the face and scalp. This type of eczema is more common in men than in women and can worsen if you use a lot of soap or often wear a hat or cap. It is characterized by red skin and oily, yellowish flakes. These flakes are mainly in your hair or eyebrows, behind or in your ears and between your eyelashes. The most well-known but also lightest form of seborrheic eczema is dandruff.
Atopic eczema (Constitutional eczema)
Atopic eczema, also called constitutional eczema, is caused by a combination of genes and environmental factors. Symptoms of atopic eczema include red, dry, scaly and itchy patches on the skin. This form of eczema can occur anywhere on your body, but you'll see it mostly on the back of the knees and on the hands and feet. During an attack, the skin may secrete fluid and bleed, and scabs may form. Further complications, such as infections, may also occur.
Contact Eczema
Contact eczema is a localized reaction that can cause redness, itching and burning where the skin has come into contact with an allergen or irritant, such as acids, cleaning products or cosmetics. Contact eczema accounts for 84-90% of work-related skin conditions.
What are the symptoms of eczema?
All the different types of eczema have the same symptoms, but your doctor can tell you which type you have. Eczema can cause the creases in your arms and legs to become dry, scaly, red, itchy and cracked. If you scratch, those spots thicken and you get cracks. If your eczema becomes inflamed, you may get painful blisters full of pus and bumps that secrete fluid, bleed and crust. You can then also get eczema on your face, neck, scalp and other parts of your body.
A severe form of eczema can keep you awake at night, making it difficult to get the recommended eight hours of sleep. This can affect both your personal life and your working life, as you are likely to be listless and tired most of the time.
How does eczema develop?
In eczema, the skin cells are less able to retain moisture and produce fats and oils. This means that the skin's function as a barrier is compromised, and the skin is susceptible to drying out, irritation and infection.
There are many different things that can lead to the development of eczema, for example :
- Food allergy or intolerance
- Your genes - some types of eczema are hereditary
- Asthma
- Use of harsh soaps and skin care products that irritate your skin
- If your body produces more IgE antibodies than it should, which can affect your immune system
- A viral infection
- If your skin does not form a strong enough barrier
- An allergy to dust mites, pollen, cats or dogs
- Stress
- Other medical conditions
- Coming into close contact with chemicals and irritants without wearing protective gloves or clothing
- Weather changes. Cold can dry out your skin, making you more susceptible to eczema.
What to do about eczema?
In almost three out of four children who suffer from eczema, the condition disappears by the time they are 7 years old. Unfortunately, some people suffer from it all their lives, but with the right treatment this need not be an insurmountable problem.
Your family doctor can refer you to a specialist for an allergy test to find out the possible cause(s). He or she may recommend a soap substitute, for example, or prescribe antibiotics or antihistamines, but in many cases there is also much you can do yourself to reduce your symptoms. To temporarily relieve the symptoms, you can put a cold wet cloth on the eczema spot to reduce the itching, but what you should mainly try to find out is what is causing your eczema. Read how to treat eczema.
Here's what you can do about eczema
1. Avoid products that can irritate your skin.
2. Take care of your skin with a moisturizer that contains manuka honey, chamomile or aloe vera. You can also choose the special eczema cream or the eczema oil from Grahams.
3. Keep track of which food products trigger your eczema and eliminate them from your menu.
4. Drink plenty of water and eat mostly fruits, vegetables and essential fatty acids.
Does this not help? Then make an appointment with your doctor; he or she can prescribe steroid creams or other healing ointments. With atopic eczema you should use emollient moisturizers every day, and during (acute) eczema attacks you use topical corticosteroids (topical steroids) and healing ointment.
Depending on the severity of your eczema, your primary care physician may refer you to a dermatologist, who can put together a customized treatment plan.
What helps against itching caused by eczema?
There are many natural remedies that can help soothe your skin if you suffer from eczema. Some of these products you may just already have in your kitchen cupboard! Read how to stop eczema itching immediately.
Coconut oil
Almost all of us have heard of this tropical wonder oil by now. Coconut oil is known as a real all-rounder, penetrates well into the skin and replenishes the moisture in your skin.
Bacteria
Healthy gut does wonders for your overall health: 80 percent of your immune system is located in your digestive zone. Healthy gut also leads to healthy skin. There are certain bacteria known for their gut-friendly properties, such as acidophilus. Acidophilus is found in sauerkraut, among other things, but you can also buy acidophilus as a dietary supplement.
Honey
Honey has been used for years because of the health-promoting properties this golden good is said to contain. Honey not only acts as an antibacterial, but also contains antioxidants and helps with certain skin complaints.[1]
Sulfur Soap
Cleaning the eczema regularly with sulfur soap, could also possibly provide relief. Sulfur soap, also known as sulfur soap or sulphur soap in English, has an extra caring and cleansing effect on irregular skin.
A soothing bath
Sometimes you just need to go back to basics. If you've tried everything and still feel lousy, take an oatmeal bath - oatmeal can soothe and hydrate your skin.
Taking an oat bath doesn't mean you have to immerse yourself in a huge tub of oatmeal. Simply put the amount of a mug of oatmeal in a cotton cloth, tie the cloth shut and place it in the bath. Keep soaking in the milky water for at least 15 minutes to feel the effect properly.



Comments
Post a Comment