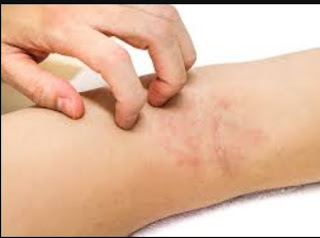
how to stop eczema itching immediately
Constitutional eczema (or atopic eczema) is a common highly itchy inflammation of the skin. The disorder usually begins in the first years of life and then disappears by puberty or even earlier. However, constitutional eczema can also continue until after puberty or start only after puberty. It is a disease for which there is a congenital "predisposition" and is associated with asthma. Read eczema on face
Who gets constitutional eczema?
Constitutional eczema is increasingly common in Western society. Women and men have an equal risk of developing the disease. About seventy percent of patients have family members with eczema, asthma or hay fever. As indicated, the symptoms usually begin in early childhood, but the first symptoms may even occur in people aged seventy years or older .
What does eczema look like?
Characteristics of constitutional eczema are:
Redness: the inflammation causes increased blood flow to the skin. Read eczema cream for face.
Itching: eczema is always itchy. Scratching temporarily relieves the itch, but over time an "itch-scratching itch cycle" develops: scratching creates new itch, which in turn leads to more scratching, and so on.
Dry skin: eczema skin is dry and scaly.
Lichenification: scratching causes the skin to thicken and the skin structures to enlarge over time.
Infection: Bacteria can settle better on eczema skin than on healthy skin. Bacteria can also proliferate in scratching wounds. Red, superficial wounds (erosions) appear, from which yellow wound fluid comes out. This fluid often dries to form yellow scabs. A bacterial infection of eczema is called impetigo. Bacterial infections can also cause pimples to form.
Blisters: during an acute exacerbation of eczema, blisters or even blisters may form; these are filled with clear fluid.
Pigmentation change: rubbing the eyes can cause a dark discoloration of the eyelids over time. When eczema calms down, areas of the skin where the eczema has been may be lighter in color than normal skin (hypopigmentation). People with darker skin types may also have a darker discoloration of the skin (hyperpigmentation). These color changes usually disappear over time.
On what parts of the skin does eczema occur?
Constitutional eczema can occur on all areas of the skin. However, a few spots are notorious. In young children, they are mainly:
face
knee hollows
elbow creases.
Later in life, other parts of the skin are also affected:
trunk
neck
backs of hands
What factors can make constitutional eczema worse?
Constitutional eczema is a condition for which there is a congenital predisposition. However, there are certain factors that can make eczema worse :
Stress
Mental and physical stress can make eczema very much worse in a short period of time. Unfortunately, avoiding stress is often easier said than done. In some cases, counseling from a psychologist may be necessary.
Dry skin
Dry skin is a major triggering factor for constitutional eczema. Especially in winter, the atmosphere at home and at work is very dry due to central heating. This, combined with inclement weather outside, can cause very dry skin. Greasing with oily creams or ointments is therefore very important. If necessary, adjust your showering behavior by not showering too hot, less often and briefly (maximum 5 minutes). Read sudden dry skin
Allergy
People with constitutional eczema have a greater risk of developing an allergy than people without constitutional eczema. In these people, a skin reaction caused by a contact allergy can trigger an outbreak of a new eczema attack.
How is it treated ?
Mild and moderately severe eczema
here how to treat eczema.
Oily ointments
Keeping the skin in good condition reduces the risk of eczema. So keeping the skin consistently well oily (which keeps the moisture in the skin up) is very important.
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroid ointment ("hormone ointment") has two good effects on eczema. First, the ointment suppresses the inflammation in the skin, so that the redness decreases. Second, the ointment has an itch-reducing effect.
Hormone ointments are very effective against eczema, but they cannot be applied indefinitely because with long-term, continuous use it can make the skin thin. In addition, the effectiveness of hormone ointments then decreases. However, if you apply the ointment according to the doctor's instructions, the risk of developing side effects is very small. Especially if a phasing-out schedule is used (applying the ointment for a few days a week and then not applying it for a few days), the risks of problems are small.
Immune system modulating ointment and cream
Since 2003, new ointments have been introduced in the Netherlands that inhibit the inflammatory response of eczema and do not contain a corticosteroid. These are Tacrolimus ointment and Pimecrolimus cream:
Tacrolimus Ointment
Tacrolimus (brand name Protopic ®) is a substance that affects the immune system. Applied in ointment, it inhibits the inflammatory response associated with eczema. One of the advantages is that the skin does not become thinner when using the product. This is in contrast to corticosteroid ointment where this can happen. A disadvantage is the risk of irritation after applying the ointment. Also, the ointment cannot be combined with sunlight. Eczema patients aged two years and older may apply the ointment.
Pimecrolimus cream
The action and application of Pimecrolimus cream are broadly similar to Tacrolimus ointment. Pimecrolimus cream (brand name: Elidel ®) has been available in the Netherlands on prescription since 2003. The ointment can also be used in eczema patients aged two years and older. Pimecrolimus cream is intended for mild to moderately severe constitutional eczema.
Tar Ointments
Tar ointment (liquor carbonis detergent) has an anti-inflammatory effect on the skin. In mild eczema, tar ointment can partially replace hormone ointments.
Antibiotics
Skin affected by eczema has a high chance of becoming infected with bacteria. Slightly infected skin can be treated by temporarily rubbing it with disinfectant cream or antibiotic ointment. If the infection is extensive and wet spots and pimples appear, a course of antibiotics may be necessary.
Wet bandages (wet-wrap method)
Wet bandages cool the warm inflamed skin and work very well against itching. Special "tube bandages" and pajamas (Tubifast ®) have been developed that can be applied at night.
The great advantage of this therapy is that the eczema can be calmed with little corticosteroid ointment and often even without corticosteroid ointment at all.
Antihistamine
If the itching persists despite the measures mentioned above, the doctor may also prescribe special itch-relieving medications. These drugs are called antihistamines.
Severe eczema
In the case of constitutional eczema that cannot be suppressed with the previously mentioned remedies, other measures must be taken. If the eczema suddenly gets worse, the dermatologist may suggest a day hospitalization. Agents that can be applied (temporarily) in severe eczema are:
Prednisone
Prednisone is usually administered as a "shock treatment", i.e. a relatively high dose is given for a few days and then stopped again. However, an appropriate follow-up policy must then be agreed.
Ciclosporin
Ciclosporin (Neoral ®) suppresses the immune response that plays an important role in eczema. The drug is often extremely effective, but can only be used for a limited time (usually several months). Many possible side effects have been described, including rise in blood pressure and kidney problems. Regular checks of blood and blood pressure are necessary. After stopping, the eczema may return strongly.
UV therapy
Eczema often responds well to sunlight. Many people with eczema therefore have fewer symptoms of their skin condition in the summer than in the winter. For these people, ultraviolet light therapy (PUVA or UVB) can sometimes offer relief when the eczema worsens.
Day treatment
One option at the Dermatology Center is day treatment. This involves a combination of tar preparations, light therapy or other ointment therapies.
Treatment with hormone ointment
Table at leaflet control and treatment eczema.
Schedule for use of hormone ointments
1 week 2x a day
1 week 1x per day
6 days consecutively 1x per day and 1 day not to use
5 days consecutively 1x daily and 2 days do not use
4 consecutive days 1x daily and 3 days do not use
1x per day for 3 consecutive days and no use for 4 days (may also be used every other day)
2 consecutive days 1x per day and 5 days without use
If it goes well, you can continue to phase out to a level where the symptoms stay away! If there is a significant worsening you should start again at the top and reduce to an optimal maintenance dosage.
Phasing out hormone ointments
After a week, you will usually see clear improvement. Before you discontinue, the skin should really have improved sufficiently: the active eczema is no longer visible and the itching has decreased.
Criteria for phasing out:
The redness decreases.
The skin feels smoother.
Itching is reduced.
How to taper off the hormone ointment.
You start your treatment by applying hormone ointment once or twice a day.
When there is a clear improvement (the active eczema is no longer visible and the itching has diminished), you will go to applying hormone ointment once a day.
If this continues to go well, go to: stop using hormone ointment for one day, apply hormone ointment for six days.
With continued improvement go to: two days stop using hormone ointment, five days do apply hormone ointment etc.
Below are a number of possibilities worked out.
Reduce to zero days or a few days of applying hormone ointment in the week, for example only on weekends. You can keep this up for months. Sometimes you can phase out to zero days. There are also people who do not succeed in reducing to zero, so you can continue to apply hormone ointment one or two days a week.
In addition to reducing the frequency of application, you can also reduce the frequency of application by changing to a less strong hormone ointment. So from a class 3 to a class 2 ointment. Discuss this with your doctor.
Do not continue tapering if there is no improvement, or if you notice that the eczema is coming back.
If the eczema flares up, go back to the schedule. When the skin is calm again, you can start tapering off again. If the flare-up occurs on consecutive stop days, stay on the same step for the following week and use the hormone ointment every other day.
Inspection of the skin is always most important. Do not taper off until the skin is calm.
Caution!
Never stop applying hormone ointment all at once!
Hormone ointment maintenance dosage
Before you start tapering off, your skin should have improved enough and remain calm. Continue until you reach a maintenance dosage of one to two days a week where your skin remains calm. This varies per period. It may be that you apply hormone ointment 5 days a week for a number of weeks in a row because the eczema has more difficulty calming down during that period. In a quiet period, for example, you only need hormone ointment two days a week.
Only if it is possible, you should stop using hormone ointment altogether and only apply neutral ointment without medication. Consult with your nurse or doctor if you need more than 100 grams of hormone ointment per week for more than three months. It may be practical to keep a schedule for yourself of the days you need to use hormone ointment.
What can you do yourself ?
Fight dry skin
For people with dry skin, frequent, long and hot showers or baths are not recommended. Do not shower too long (up to five minutes). Use lukewarm water (no more than thirty degrees) and shower no more than once a day with a ph-neutral and perfume-free shower or bath oil (for example, Balneum Hermal or Sebamed).
If you have very dry skin or active eczema, do not shower or bathe more than twice a week. For baths, do not bathe too hot, no longer than fifteen minutes and add a ph-neutral and perfume-free bath oil to the water. Then dry the skin by patting. It is wise to then grease the skin with an oily ointment. This procedure is always important, even when you do not have eczema.
Avoid irritating and occlusive clothing
Irritating and rough textiles such as wool can exacerbate eczema itching. Non-ventilating clothing (synthetic materials) produces a sweltering, and therefore itch-inducing effect. Wearing undertextiles and pajamas made of natural silk (e.g. Dermasilk/Dermacura) or organic cotton can therefore alleviate symptoms.
Sun
Sunlight often has a positive effect on eczema complaints. However, be careful not to overexpose yourself to sunlight and certainly not to burn. Too much sun damage to the skin can eventually lead to the development of skin cancer.
Pillar 1: Recognize triggering factors,
avoid, reduce, protect.
Pillar 2: skin care 365 days a year at least twice a day topical ointment.
Pillar 3: treating eczema with hormone ointment according to the phasing-out schedule (see also "How often can I use hormone ointment?").
Skin care
Neutral ointments are available on doctor's prescription. The pharmacy makes it itself or orders it from a wholesaler. Because reimbursements are adjusted every year, we have noticed lately that some insurers no longer reimburse all neutral ointments.
Ointment technique
Distribute the ointment in small amounts on a body part and then spread it.
Spread a small amount of ointment between your hands, then apply it to the skin and spread it.
For ointments with medications, wear gloves if necessary. For basic ointments, gloves are not necessary.
Neutral ointment is never a replacement for hormone ointment. But the basis of treatment.
Hormone ointment and neutral ointment combination
Apply as follows if you use both hormone ointment and topical ointment:
First treat the eczema spots with the prescribed hormone ointment.
Leave this ointment on for at least one hour. Then apply the ointment to the entire skin.
Itching
Children with eczema have a lowered skin irritation threshold. They experience itching and skin irritation faster than people without eczema. To counteract the itching, they start rubbing and scratching. This gives a brief relief but this relief is temporary.
Eventually, the eczema gets worse because of the scratching. The skin becomes damaged, so that certain substances, such as bacteria and fungi, can penetrate the skin more easily. This causes new irritations, damage and infections. This can make the eczema and itching worse. Moreover, the repair of the skin eventually leads to itching again. The vicious circle of itching-scratching-itching is thus maintained.
How to stop eczema itching immediately ? home remedies
- Cover the skin to limit the damage from any scratching and allow the ointment/cream to work properly.
- Extra oil the skin; the drier the skin, the more itchy it is.
- Seek distraction and alternatives (e.g., rubbing or patting the skin) to limit scratching. If you continue to scratch, you are perpetuating the condition and constantly damaging already damaged skin.
- Cooling also reduces itching (for example, by using cold packs or a rolled up towel in the freezer). Just make sure it doesn't get directly on bare skin.
- Sleep in a cool room; heat often causes an increase in itching.
- Wear cotton clothing.
- Do not use fabric softeners; this will always remain in the clothing and will undoubtedly cause itching.
- If wearing clean clothes or sleeping between clean sheets makes you itch, it may be that the detergent you are using is irritating the skin. Bell or Neutral detergent is then an alternative. Another option is to rinse the detergent container well with a little vinegar. Half a cup of vinegar in the softener tray is enough to remove the last of the soap residue and it does not leave a vinegar smell. The vinegar also softens the laundry.
- Use as little water as possible; so shower/bath and wash your hands as little as possible. It is advisable to use a private towel at home or in the work situation. This is to avoid coming into contact with soap residues that remain in the towel and can therefore cause itching again.
- When wearing household gloves always wear a cotton glove inside. Household gloves alone can cause a scalding reaction and can lead to an increase in itching. There are special gloves with a cotton inside for sale at the pharmacy/drugstore (Sempersoft from the company Van de Bend).
- Be careful when cleaning vegetables/fruit and peeling potatoes. The juice of vegetables, fruits and potatoes is also irritating to the skin and can therefore cause itching.
- Protect the skin extra in case of frost because the cold dries out the skin and therefore causes itching.
- Ensure sufficient rest and regularity. When there is a lot of stress or irregularity, this can aggravate the skin condition and make the itching worse. So listen to your body and get enough rest. If necessary, relaxation exercises can help you to unwind.



Comments
Post a Comment